AIって結局何なのかよく分からないので、とりあえず100日間勉強してみた Day90
経緯についてはこちらをご参照ください。
■本日の進捗
- RNNの学習を理解
■はじめに
今回も「ゼロから作るDeep Learning② 自然言語処理編(オライリー・ジャパン)」から学んでいきます。
今回は、前回実装した再帰型ニューラルネットワークを学習できる形に実装していきます。
■RNNの学習
これまでも用いてきた簡易版PTBデータセットを再帰型ニューラルネットワークで学習するように実装してみます。ただし、データセットは学習の軽量化のため、最初の1000個を用いるようにします。
import sys
import os
sys.path.append('..')
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pickle
from sklearn.utils.extmath import randomized_svd
import collections
GPU = False
# setting for PTB dataset
key_file = {
'train':'ptb.train.txt',
'test':'ptb.test.txt',
'valid':'ptb.valid.txt'
}
save_file = {
'train':'ptb.train.npy',
'test':'ptb.test.npy',
'valid':'ptb.valid.npy'
}
vocab_file = 'ptb.vocab.pkl'
dataset_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
mid_path = '..\..\Download_Dataset\lstm-master\data'
def load_vocab():
vocab_path = os.path.join(dataset_dir, vocab_file)
print(vocab_path)
if os.path.exists(vocab_path):
with open(vocab_path, 'rb') as f:
word_to_id, id_to_word = pickle.load(f)
return word_to_id, id_to_word
word_to_id = {}
id_to_word = {}
data_type = 'train'
file_name = key_file[data_type]
file_path = os.path.join(dataset_dir, mid_path, file_name)
words = open(file_path).read().replace('\n', '<eos>').strip().split()
for i, word in enumerate(words):
if word not in word_to_id:
tmp_id = len(word_to_id)
word_to_id[word] = tmp_id
id_to_word[tmp_id] = word
with open(vocab_path, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump((word_to_id, id_to_word), f)
return word_to_id, id_to_word
def load_data(data_type='train'):
if data_type == 'val': data_type = 'valid'
save_path = dataset_dir + '\\' + save_file[data_type]
print('save_path:', save_path)
word_to_id, id_to_word = load_vocab()
if os.path.exists(save_path):
corpus = np.load(save_path)
return corpus, word_to_id, id_to_word
file_name = key_file[data_type]
file_path = os.path.join(dataset_dir, mid_path, file_name)
words = open(file_path).read().replace('\n', '<eos>').strip().split()
corpus = np.array([word_to_id[w] for w in words])
np.save(save_path, corpus)
return corpus, word_to_id, id_to_word
class Embedding:
def __init__(self, W):
self.params = [W]
self.grads = [np.zeros_like(W)]
self.idx = None
def forward(self, idx):
W, = self.params
self.idx = idx
out = W[idx]
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dW, = self.grads
dW[...] = 0
if GPU:
np.scatter_add(dW, self.idx, dout)
else:
np.add.at(dW, self.idx, dout)
return None
def softmax(x):
if x.ndim == 2:
x = x - x.max(axis=1, keepdims=True)
x = np.exp(x)
x /= x.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
elif x.ndim == 1:
x = x - np.max(x)
x = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
return x
class RNN:
def __init__(self, Wx, Wh, b):
self.params = [Wx, Wh, b]
self.grads = [np.zeros_like(Wx), np.zeros_like(Wh), np.zeros_like(b)]
self.cache = None
def forward(self, x, h_prev):
Wx, Wh, b = self.params
t = np.dot(h_prev, Wh) + np.dot(x, Wx) + b
h_next = np.tanh(t)
self.cache = (x, h_prev, h_next)
return h_next
def backward(self, dh_next):
Wx, Wh, b = self.params
x, h_prev, h_next = self.cache
dt = dh_next * (1 - h_next ** 2)
db = np.sum(dt, axis=0)
dWh = np.dot(h_prev.T, dt)
dh_prev = np.dot(dt, Wh.T)
dWx = np.dot(x.T, dt)
dx = np.dot(dt, Wx.T)
self.grads[0][...] = dWx
self.grads[1][...] = dWh
self.grads[2][...] = db
return dx, dh_prev
class TimeRNN:
def __init__(self, Wx, Wh, b, stateful=False):
self.params = [Wx, Wh, b]
self.grads = [np.zeros_like(Wx), np.zeros_like(Wh), np.zeros_like(b)]
self.layers = None
self.h, self.dh = None, None
self.stateful = stateful
def forward(self, xs):
Wx, Wh, b = self.params
N, T, D = xs.shape
D, H = Wx.shape
self.layers = []
hs = np.empty((N, T, H), dtype='f')
if not self.stateful or self.h is None:
self.h = np.zeros((N, H), dtype='f')
for t in range(T):
layer = RNN(*self.params)
self.h = layer.forward(xs[:, t, :], self.h)
hs[:, t, :] = self.h
self.layers.append(layer)
return hs
def backward(self, dhs):
Wx, Wh, b = self.params
N, T, H = dhs.shape
D, H = Wx.shape
dxs = np.empty((N, T, D), dtype='f')
dh = 0
grads = [0, 0, 0]
for t in reversed(range(T)):
layer = self.layers[t]
dx, dh = layer.backward(dhs[:, t, :] + dh)
dxs[:, t, :] = dx
for i, grad in enumerate(layer.grads):
grads[i] += grad
for i, grad in enumerate(grads):
self.grads[i][...] = grad
self.dh = dh
return dxs
def set_state(self, h):
self.h = h
def reset_state(self):
self.h = None
class TimeEmbedding:
def __init__(self, W):
self.params = [W]
self.grads = [np.zeros_like(W)]
self.layers = None
self.W = W
def forward(self, xs):
N, T = xs.shape
V, D = self.W.shape
out = np.empty((N, T, D), dtype='f')
self.layers = []
for t in range(T):
layer = Embedding(self.W)
out[:, t, :] = layer.forward(xs[:, t])
self.layers.append(layer)
return out
def backward(self, dout):
N, T, D = dout.shape
grad = 0
for t in range(T):
layer = self.layers[t]
layer.backward(dout[:, t, :])
grad += layer.grads[0]
self.grads[0][...] = grad
return None
class TimeAffine:
def __init__(self, W, b):
self.params = [W, b]
self.grads = [np.zeros_like(W), np.zeros_like(b)]
self.x = None
def forward(self, x):
N, T, D = x.shape
W, b = self.params
rx = x.reshape(N*T, -1)
out = np.dot(rx, W) + b
self.x = x
return out.reshape(N, T, -1)
def backward(self, dout):
x = self.x
N, T, D = x.shape
W, b = self.params
dout = dout.reshape(N*T, -1)
rx = x.reshape(N*T, -1)
db = np.sum(dout, axis=0)
dW = np.dot(rx.T, dout)
dx = np.dot(dout, W.T)
dx = dx.reshape(*x.shape)
self.grads[0][...] = dW
self.grads[1][...] = db
return dx
class TimeSoftmaxWithLoss:
def __init__(self):
self.params, self.grads = [], []
self.cache = None
self.ignore_label = -1
def forward(self, xs, ts):
N, T, V = xs.shape
if ts.ndim == 3:
ts = ts.argmax(axis=2)
mask = (ts != self.ignore_label)
xs = xs.reshape(N * T, V)
ts = ts.reshape(N * T)
mask = mask.reshape(N * T)
ys = softmax(xs)
ls = np.log(ys[np.arange(N * T), ts])
ls *= mask
loss = -np.sum(ls)
loss /= mask.sum()
self.cache = (ts, ys, mask, (N, T, V))
return loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
ts, ys, mask, (N, T, V) = self.cache
dx = ys
dx[np.arange(N * T), ts] -= 1
dx *= dout
dx /= mask.sum()
dx *= mask[:, np.newaxis]
dx = dx.reshape((N, T, V))
return dx
class SimpleRnnlm:
def __init__(self, vocab_size, wordvec_size, hidden_size):
V, D, H = vocab_size, wordvec_size, hidden_size
rn = np.random.randn
embed_W = (rn(V, D) / 100).astype('f')
rnn_Wx = (rn(D, H) / np.sqrt(D)).astype('f')
rnn_Wh = (rn(H, H) / np.sqrt(H)).astype('f')
rnn_b = np.zeros(H).astype('f')
affine_W = (rn(H, V) / np.sqrt(H)).astype('f')
affine_b = np.zeros(V).astype('f')
self.layers = [
TimeEmbedding(embed_W),
TimeRNN(rnn_Wx, rnn_Wh, rnn_b, stateful=True),
TimeAffine(affine_W, affine_b)
]
self.loss_layer = TimeSoftmaxWithLoss()
self.rnn_layer = self.layers[1]
self.params, self.grads = [], []
for layer in self.layers:
self.params += layer.params
self.grads += layer.grads
def forward(self, xs, ts):
for layer in self.layers:
xs = layer.forward(xs)
loss = self.loss_layer.forward(xs, ts)
return loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
dout = self.loss_layer.backward(dout)
for layer in reversed(self.layers):
dout = layer.backward(dout)
return dout
def reset_state(self):
self.rnn_layer.reset_state()
corpus, word_to_id, id_to_word = load_data('train')
corpus = corpus[:1000]
batch_size = 10
wordvec_size = 100
hidden_size = 100
time_size = 5
lr = 0.1
max_epoch = 1000
vocab_size = len(word_to_id)
xs = corpus[:-1]
ts = corpus[1:]
data_size = len(xs)
def create_batch(xs, ts, batch_size, time_size):
batch_x = np.zeros((batch_size, time_size), dtype=np.int32)
batch_t = np.zeros((batch_size, time_size), dtype=np.int32)
for i in range(batch_size):
start_idx = np.random.randint(0, len(xs) - time_size)
batch_x[i] = xs[start_idx:start_idx + time_size]
batch_t[i] = ts[start_idx:start_idx + time_size]
return batch_x, batch_t
model = SimpleRnnlm(vocab_size, wordvec_size, hidden_size)
loss_list = []
for epoch in range(max_epoch):
total_loss = 0
for _ in range(data_size // (batch_size * time_size)):
batch_x, batch_t = create_batch(xs, ts, batch_size, time_size)
loss = model.forward(batch_x, batch_t)
model.backward()
for param, grad in zip(model.params, model.grads):
param -= lr * grad
total_loss += loss
avg_loss = total_loss / (data_size // (batch_size * time_size))
loss_list.append(avg_loss)
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{max_epoch}, Loss: {avg_loss:.4f}")
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(range(1, max_epoch + 1), loss_list, marker='o')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Reccurent Neural Network learning')
plt.show()
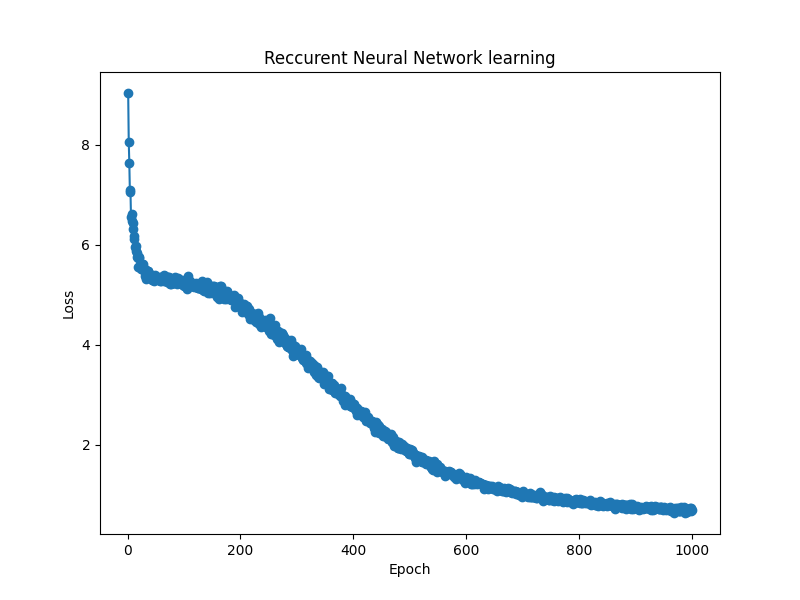
損失が0付近に収束していて、モデルが学習できていることが分かりました。
■言語モデルの評価指標
言語モデルの評価指標としてPerplexityを導入します。
$$ L = \ – \frac{1}{N} \displaystyle \sum_n \sum_k t_{nk} \log y_{nk} $$
$$ \mathrm{perplexity} = e^{L} $$
この指標は数字が小さいほどモデル性能が高いと解釈でき、次に取り得る選択肢としての数を示しています。つまり、perplexity=100ならモデルが単語を選ぶのに100個の選択肢があり、最小値1ならば一意に決まるということです。
先ほど学習させたモデルに、エポック毎にperplexityを出し、同様にプロットさせてみます。
loss_list = []
ppl_list = []
loss_count = 0
for epoch in range(max_epoch):
total_loss = 0
for _ in range(data_size // (batch_size * time_size)):
batch_x, batch_t = create_batch(xs, ts, batch_size, time_size)
loss = model.forward(batch_x, batch_t)
model.backward()
for param, grad in zip(model.params, model.grads):
param -= lr * grad
total_loss += loss
loss_count += 1
avg_loss = total_loss / (data_size // (batch_size * time_size))
loss_list.append(avg_loss)
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{max_epoch}, Loss: {avg_loss:.4f}")
ppl = np.exp(total_loss / loss_count)
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{max_epoch}, Perplexity: {ppl}")
ppl_list.append(float(ppl))
loss_count = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(range(1, max_epoch + 1), loss_list, marker='o', color='green', label='Loss')
plt.plot(range(1, max_epoch + 1), ppl_list, marker='o', color='orange', label='Perplexity')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend()
plt.ylim(-0.5, 20.5)
plt.title('Reccurent Neural Network perplexity')
plt.show()
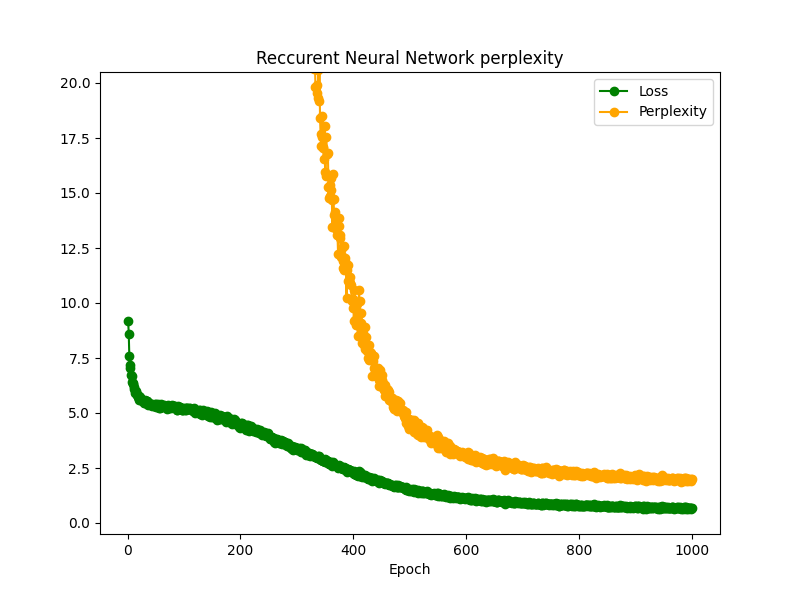
1Epoch目のPerplexityは500を超えるのでy軸範囲は調整しています。損失関数の値が下がってモデルが学習するに従って、Perplexityの値も下がっていることが確認できます。
今回の場合では、Perplexityは1.8程度まで下がっています。単語の選択肢として1.8個のみになっているというのは、モデルがある程度高い確信を持って単語を提示できることを示しています。
■おわりに
今回は再帰型ニューラルネットワークを学習させるように実装し、言語モデルの評価指標を導入することができました。
■参考文献
- Andreas C. Muller, Sarah Guido. Pythonではじめる機械学習. 中田 秀基 訳. オライリー・ジャパン. 2017. 392p.
- 斎藤 康毅. ゼロから作るDeep Learning Pythonで学ぶディープラーニングの理論と実装. オライリー・ジャパン. 2016. 320p.
- 斎藤 康毅. ゼロから作るDeep Learning② 自然言語処理編. オライリー・ジャパン. 2018. 432p.
- ChatGPT. 4o mini. OpenAI. 2024. https://chatgpt.com/
- API Reference. scikit-learn.org. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/api/index.html
- PyTorch documentation. pytorch.org. https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/index.html
- Keiron O’Shea, Ryan Nash. An Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks. https://ar5iv.labs.arxiv.org/html/1511.08458
- API Reference. scipy.org. 2024. https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/index.html